RIB ( Routing Information Base )
FIB ( Forwarding Information Base )
LIB ( Label Information Base )
LFIB ( Label Forwarding Instance Base )
Adjacency table
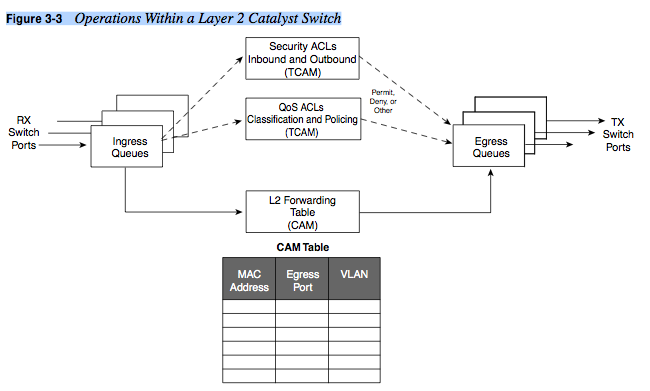
CAM table
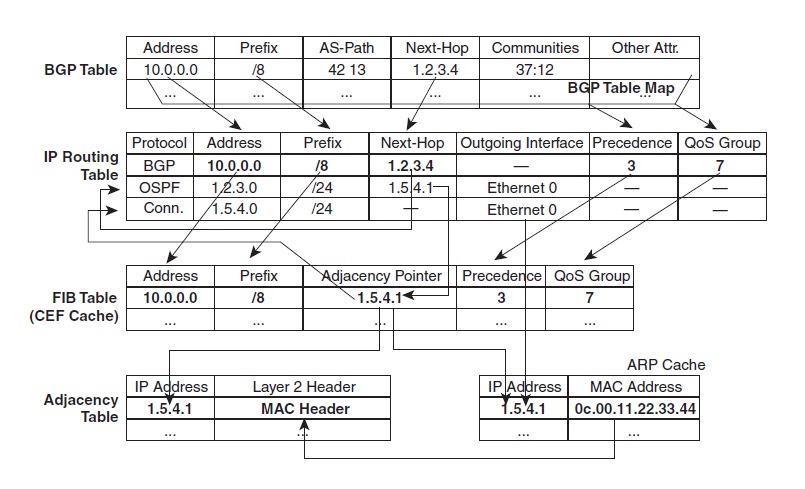
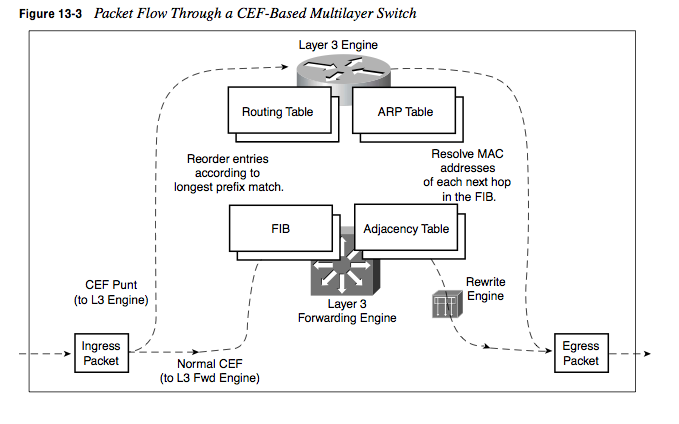
RIB : The routing table contain all the informations regarding the creation of routing lookup by matching a destination address to the next hop but without the egress interface.
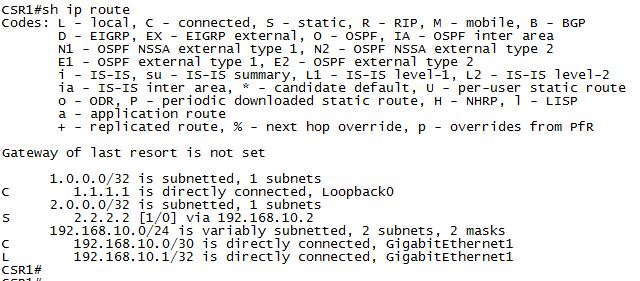
Example : when you issue the command #show ip route the output that we see is the routing table.
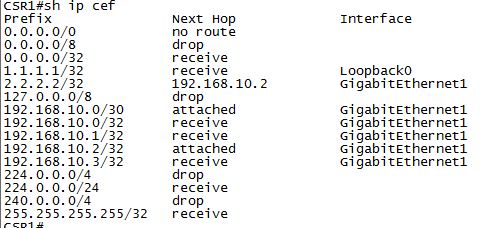
FIB : The Forwarding information base store all the destination prefix from the RIB
Example : when you issue the command #show ip cef the output that we see is the forwarding table.
LIB :
LFIB :
Adjacency table : The adjacency table is constructed at the same time as the RIB is populate using the ip of the next hop and ARP for L3 to L2 mapping to translate the ip to their corresponding layer 2 address. ARP table is used to populate IP-MAC info in both CAM and Adjacency Tables.
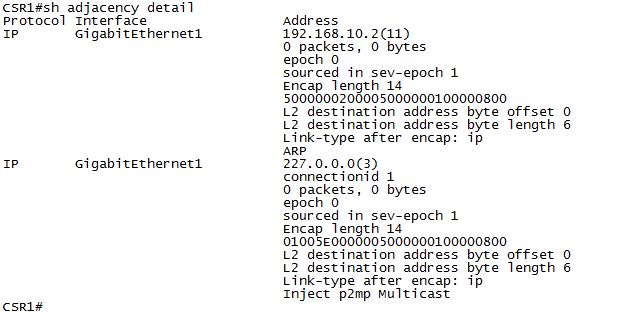
Example : when you issue the command #show adjacency the output that we see is :.

Example : when you issue the command #show adjacency detail the output that we see is :
This table describes key fields in the show adjacency [interface-type interface-number] internal command. Link from Cisco
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
192.168.10.2(11) |
IP address of the next-hop interface. The value in parenthesis refers to the “refCount” or the number of times that this adjacency is pointed to by FIB entries. The same value appears later in the entry. |
0 packets, 0 bytes |
Use the ip cef accounting command to enable packet and byte counters. |
0060471E91D8003071D310000800 |
The first twelve characters are the MAC address of the destination next-hop interface. The next twelve characters represent the MAC address of the source interface of the packet. (In other words, the outbound interface of the local router). The last four characters represent the well-known Ethertype value 0x0800 for IP (with Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) encapsulation). |
003071D310000800 |
MAC address and well-known Ethertype value 0x0800 for IP (with ARPA encapsulation) of the source interface of the packet. (In other words, the outbound interface of the local router). |
ARP 03:57:00 |
ARP indicates how the entry is discovered. The timestamp indicates how long to go before the entry times out. |
Epoch: 1 |
CEF adjacency table Epoch information. Use the show ip cef epoch command to display the epoch information for the adjacency table and all FIB tables. |
Fast adjacency enabled |
An FIB entry caches an adjacency for a next-hop interface when not doing load-sharing over multiple active paths. A fast adjacency facilitates faster switching of packets. |
Adjacency pointer 0x62515AC0 |
|
refCount 7 |
The number of references to the adjacency that are currently stored in the router’s memory. There is one for each corresponding entry in the CEF table, plus a few others for a variety of reasons (such as one for the code that performs the show adjacency command). |
Connection Id 0x0 |
|
Bucket 236 |
Another description i found from a user in a forum : The Adjacency table records IP address and Layer 2 header for the IP and then references the TCAM table and at this point the switch will have enough information to rewrite the packets headers and send them out the egress port….. The idea is that all of the information is loaded into the Adjacency table & TCAM table as these are run on the ASIC’s which makes it hardware/wire speed Layer 3/MLS switching.
CAM table : CAM table records the incoming packet’s MAC address, Port & VLAN.to enable Switching at Layer 2.
Example : when you issue the command #show ip arp the output that we see is the ARP table.