Multicast are use to address a number of hosts on a network (one-to-many or many-to-many distribution).
Group communication may either be application layer multicast or network assisted multicast, where the latter makes it possible for the source to efficiently send to the group in a single transmission. Copies are automatically created in other network elements, such as routers, switches and cellular network base stations, but only to network segments that currently contain members of the group.
How does it happen : Hardware Multicasting and IP multicasting and the Mapping process .
When the network card picks up a packet which has a destination MAC that matches any of the multicast MAC addresses, it will pass it to the upper layers for further processing
Ethernet uses the low-order bit of the high-order octet to distinguish conventional unicast addresses from multicast addresses. A unicast would have this bit set to ZERO (0), whereas a multicast would be set to ONE (1)
00:26:cb:a8:db:d2 in this case this is a unicast address cause the the low-order of the higher octect is 0 .
01:00:5E:00:00:05 is an multicast ause the the low-order of the higher octect is 1.
Now we know to differentiate an multicast from an unicast from the low-order hight octect bit ! 00 = unicast 01 = multicast .
With IP multicasting the hardware multicasting MAC address is mapped to an IP Address. Once Layer 2 (Datalink) picks the multicast packet from the network (because it recognises it, as the destination MAC address is a multicast) it will strip the MAC addresses off and send the rest to the above layer, which is the Network Layer .
the Network Layer needs to be able to understand it’s dealing with a multicast, so the IP address is set in a way that allows the computer to see it as a multicast datagram. A host may send multicast datagrams to a multicast group without being a member.
MAPPING IP MULTICAST TO ETHERNET MULTICAST
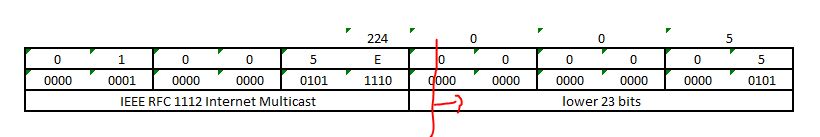
To map an IP Multicast address to the corresponding Hardward/Ethernet multicast address, place the low-order 23 bits of the IP multicast address into the low-order 23 bits of the special Ethernet multicast address
IP Multicast uses Class D IP addresses 224.0.0.0 239.255.255.255.255
| 224.0.0.0 | Base address (reserved) |
| 224.0.0.1 | The All Hosts multicast group addresses all hosts on the same network segment. |
| 224.0.0.2 | The All Routers multicast group addresses all routers on the same network segment. |
| 224.0.0.4 | This address is used in the Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) to address multicast routers. |
| 224.0.0.5 | The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) All OSPF Routers address is used to send Hello packets to all OSPF routers on a network segment. |
| 224.0.0.6 | The OSPF All Designated Routers “”(DR)”” address is used to send OSPF routing information to designated routers on a network segment. |
| 224.0.0.9 | The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) version 2 group address is used to send routing information to all RIP2-aware routers on a network segment. |
| 224.0.0.10 | The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) group address is used to send routing information to all EIGRP routers on a network segment. |
| 224.0.0.13 | Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Version 2 |
| 224.0.0.18 | Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) |
| 224.0.0.19 – 21 | IS-IS over IP |
| 224.0.0.22 | Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) version 3[2] |
| 224.0.0.102 | Hot Standby Router Protocol version 2 (HSRPv2) / Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) |
| 224.0.0.107 | Precision Time Protocol (PTP) version 2 peer delay measurement messaging |
| 224.0.0.251 | Multicast DNS (mDNS) address |
| 224.0.0.252 | Link-local Multicast Name Resolution (LLMNR) address |
| 224.0.0.253 | Teredo tunneling client discovery address[3] |
| 224.0.1.1 | Network Time Protocol clients listen on this address for protocol messages when operating in multicast mode. |
| 224.0.1.22 | Service Location Protocol version 1 general |
| 224.0.1.35 | Service Location Protocol version 1 directory agent |
| 224.0.1.39 | The Cisco multicast router AUTO-RP-ANNOUNCE address is used by RP mapping agents to listen for candidate announcements. |
| 224.0.1.40 | The Cisco multicast router AUTO-RP-DISCOVERY address is the destination address for messages from the RP mapping agent to discover candidates. |
| 224.0.1.41 | H.323 Gatekeeper discovery address |
| 224.0.1.129 – 132 | Precision Time Protocol (PTP) version 1 messages (Sync, Announce, etc.) except peer delay measurement |
| 224.0.1.129 | Precision Time Protocol (PTP) version 2 messages (Sync, Announce, etc.) except peer delay measurement |
| 239.255.255.250 | Simple Service Discovery Protocol address |
| 239.255.255.253 | Service Location Protocol version 2 address |